Efficiency and Throughput Optimization of Bulk Handling Cranes
Efficiency and Throughput Optimization of Stackers, Ship Loaders, and Reclaimer Cranes
In the world of bulk materials handling, optimizing the efficiency and throughput of machinery like stackers, ship loaders, and reclaimer cranes is critical. These machines play an integral role in port terminals, stockyards, and mining operations where high productivity and low downtime determine profitability. Therefore, this article explores strategies to maximize operational efficiency, minimize costs, and enhance throughput, while ensuring equipment longevity and reliability.
Introduction to Bulk Handling Equipment
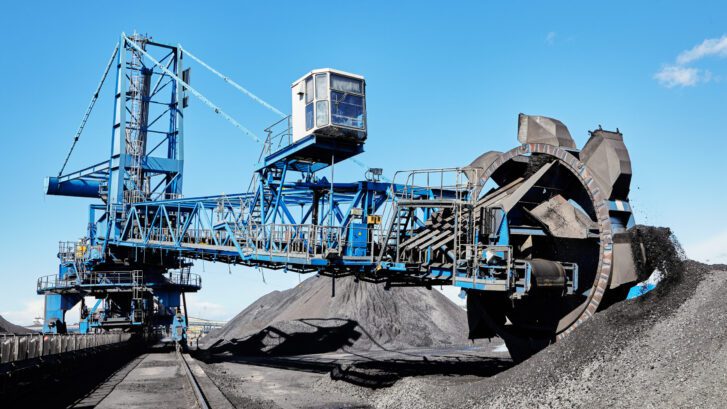
Stackers, ship loaders, and reclaimer cranes are the backbone of large-scale material handling systems. Stackers are used to pile bulk materials systematically in stockyards. In comparison, ship loaders transfer bulk materials onto vessels for export, while reclaimer cranes retrieve materials from stockpiles and deliver them for further processing or transport.
Due to their scale and operational demands, these machines require constant performance optimization to meet the growing global demand for commodities like coal, iron ore, grains, and minerals. Notably, efficiency improvements not only lead to higher output but also reduce operational costs and carbon footprints, aligning operations with modern sustainability goals.
Factors Affecting Efficiency and Throughput
Before diving into optimization strategies, it’s essential to understand the main factors influencing the efficiency and throughput of stackers, ship loaders, and reclaimers:
- Equipment Design: The structure, materials, and capacity of machinery impact operational efficiency.
- Maintenance Practices: Proper, regular maintenance minimizes downtime.
- Automation and Control Systems: Smart systems improve precision and reduce human error.
- Material Characteristics: Flowability, moisture content, and size affect handling performance.
- Operator Skill: Well-trained operators maximize productivity and minimize risks.
By addressing each of these factors, operators can significantly enhance equipment performance.
Strategies for Optimizing Stackers
1. Implement Advanced Control Systems
Modern stackers equipped with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems allow for automated stacking patterns, precise material placement, and reduced material degradation. Consequently, advanced software can analyze stockpile geometry, optimize material layering, and manage throughput.
2. Upgrade to Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
VFDs allow precise control of stacker movement, reducing energy consumption and wear. Moreover, speed adjustments according to material flow conditions ensure smoother operations and minimize mechanical stress.
3. Regular Preventive Maintenance
Proactive maintenance schedules—rather than reactive repairs—ensure that minor issues are addressed before they escalate into costly breakdowns. Additionally, regular inspection of conveyor belts, gearboxes, motors, and structural components is vital.
4. Implement Stockpile Management Systems
Optimized stockpile management prevents material segregation and maximizes space utilization. Furthermore, sophisticated software can map out the most efficient stacking configurations, reducing rehandling and spillage.
Strategies for Optimizing Ship Loaders
1. High-Precision Positioning Systems
Ship loaders equipped with laser-based or GPS-based positioning systems can precisely align with a vessel’s hatch, reducing loading times and minimizing the risk of spillage. As a result, this reduces demurrage charges and enhances overall throughput.
2. Increase Machine Mobility and Flexibility
Design features like luffing booms, telescopic conveyors, and slewing mechanisms allow ship loaders to handle different vessel sizes and configurations with ease. Consequently, enhancing the loader’s range of motion improves cycle times and operational adaptability.
3. Dust Suppression Systems
Environmental compliance is a growing priority. Efficient dust suppression systems improve site safety and reduce material loss during loading operations. Therefore, water misting systems, enclosed booms, and dust collectors are effective tools.
4. Optimize Conveyor Systems
Ship loader conveyors should be designed for high belt speeds and low resistance. By using high-tension, low-weight belts and aerodynamic idlers, operators can reduce power consumption and enhance throughput.
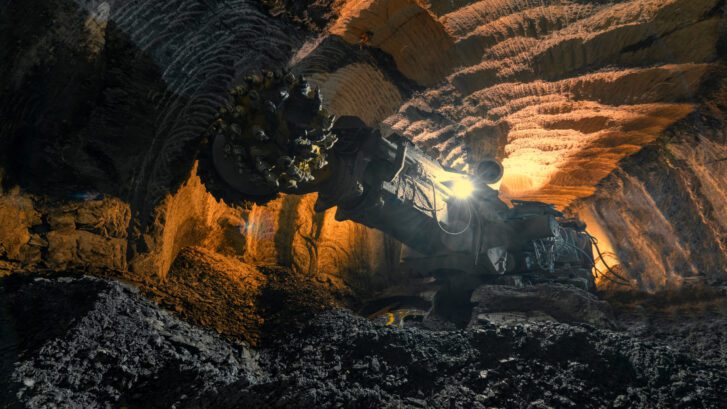
Strategies for Optimizing Reclaimer Cranes
1. Automate Reclaiming Processes
Automated reclaimers use radar, laser scanners, and real-time data analytics to perform material recovery tasks without manual input. As a result, automation reduces operational variability and increases consistency in reclaim rates.
2. Upgrade Bucket Designs
Advanced bucket designs, such as those optimized for different material densities and moisture levels, improve material pickup efficiency and reduce spillage. Moreover, wear-resistant materials also prolong bucket life.
3. Implement Condition Monitoring
Using IoT sensors and predictive analytics, operators can monitor the health of motors, gearboxes, and structural components. Consequently, predictive maintenance prevents unexpected failures and keeps reclaimers operating at peak efficiency.
4. Optimize Path Planning
Sophisticated path planning algorithms can minimize travel distances, reduce cycle times, and prevent material degradation. Proper planning, therefore, ensures uniform material recovery and stockyard balance.
Case Studies: Efficiency Improvements in Action
Case Study 1: Stackers in a Coal Export Terminal
At a major coal export terminal, introducing automated stacking systems improved stockpile management by 25%. In addition, implementing VFDs reduced energy costs by 15%, while predictive maintenance reduced downtime incidents by 30% over a 12-month period.
Case Study 2: Ship Loader Optimization at an Iron Ore Port
A ship loader upgrade project, including the installation of an extendable boom and dust suppression systems, reduced average vessel loading times by 18%. Moreover, dust emissions dropped by 40%, helping the port achieve ISO 14001 certification.
Case Study 3: Automated Reclaimer in a Steel Plant
In a steel manufacturing facility, transitioning to an automated bucket wheel reclaimer increased throughput by 22%. Additionally, predictive analytics on gearbox performance reduced emergency maintenance events by 60%, significantly lowering operational costs.
Emerging Trends in Bulk Handling Optimization
Digital Twin Technology
Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets—allow operators to simulate scenarios, predict equipment behavior, and optimize performance without risking real-world assets. Consequently, they provide invaluable insights into throughput improvement strategies.
AI and Machine Learning
AI algorithms can predict material flow rates, suggest optimal loading patterns, and alert operators to anomalies before they cause issues. Furthermore, machine learning models become increasingly accurate over time, offering smarter operational strategies.
Sustainable Operations
There is an increasing demand for eco-friendly bulk handling operations. Electrification of drives, solar-powered auxiliary systems, and efficient dust management not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance operational reputations.
Best Practices for Continuous Improvement
- Regular Training Programs: Equip operators and maintenance personnel with up-to-date knowledge of equipment features, safety standards, and efficiency techniques.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Collect operational data through SCADA systems and IoT sensors and use it to drive continuous improvements.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between engineering, operations, and maintenance teams to identify bottlenecks and brainstorm solutions.
- Vendor Partnerships: Collaborate with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) for updates, retrofits, and technical support to keep machinery at peak performance.
- Benchmarking and KPIs: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) like loading rate, downtime hours, energy usage, and maintenance frequency to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion: Building a Future of High-Efficiency Bulk Handling
Optimizing the efficiency and throughput of stackers, ship loaders, and reclaimer cranes is essential for any port, mining, or industrial operation seeking to remain competitive. By leveraging smart technologies, implementing robust maintenance programs, and investing in operator training, facilities can achieve significant improvements in operational efficiency, environmental compliance, and profitability.
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, safety, and precision, continuous optimization is not merely a competitive advantage—rather, it is a necessity. Companies that prioritize innovation and data-driven strategies will lead the future of bulk material handling, setting new benchmarks for what these powerful machines can achieve.