key differences between heavy-duty and standard encoders
A Comprehensive Guide to Heavy-Duty vs. Standard Encoders
Introduction
Encoders play a crucial role in modern industries by translating mechanical movement into readable electronic signals. These signals provide essential data on position, speed, and direction, allowing automated systems to function efficiently. However, not all encoders serve the same purpose or withstand the same environments. Two primary types exist: heavy-duty encoders and standard encoders.
While both encoder types convert motion into information, their construction, durability, and operational capacity differ significantly. This article will thoroughly compare heavy-duty and standard encoders, focusing on key aspects like durability, environmental resistance, application suitability, and performance.
What Are Encoders, and Why Do They Matter?
Encoders translate mechanical motion into electrical signals that machines or automated systems use to track motion. This conversion is crucial in various industries such as manufacturing, robotics, automotive, and more.
However, the environments in which these encoders operate vary widely. Some work in controlled indoor settings, while others face harsh outdoor or industrial conditions. Heavy-duty and standard encoders meet these different demands.
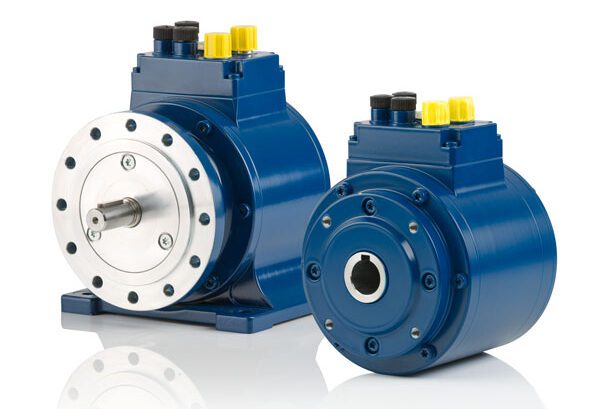
Heavy-Duty Encoders: The Industrial Workhorses
1. Design and Durability
Manufacturers design heavy-duty encoders to handle tough industrial environments. They use durable materials like stainless steel or aluminum to ensure these encoders endure extreme conditions. Their robust construction includes protective casings that shield internal components from dust, debris, and moisture.
For example, industries like mining, oil, and steel production subject equipment to high levels of mechanical stress. Heavy-duty encoders are ideal for these settings because they include:
- Sealed bearings to prevent contamination.
- Reinforced housings to resist corrosion and physical damage.
- Strong shafts that can handle high torque and mechanical loads.
This rugged construction makes heavy-duty encoders suitable for environments where standard encoders would fail.
2. Extreme Environmental Resistance
Heavy-duty encoders are engineered to function in extreme conditions. They often come with higher ingress protection (IP) ratings—typically IP67 or above—demonstrating their ability to resist dust and water. Some can even handle full immersion or operate under high-pressure washdowns.
In industries where temperature fluctuations are common, such as outdoor operations or steel plants, heavy-duty encoders perform reliably. They withstand extreme heat, freezing cold, and continuous mechanical vibration, environments that would compromise a standard encoder.
3. Applications in Harsh Industries
Heavy-duty encoders excel in industries such as:
- Mining and Quarrying: Mining equipment like crushers and conveyors operate in dirty, abrasive environments. Heavy-duty encoders ensure precise movement tracking and operational accuracy.
- Steel Mills: High temperatures and aggressive environments in steel mills demand encoders that can handle extreme heat without failure.
- Cranes and Heavy Machinery: Equipment like cranes must operate under constant vibration, heavy loads, and outdoor exposure. Heavy-duty encoders withstand these conditions while maintaining accuracy.
4. Longevity and Maintenance
Heavy-duty encoders last longer, even when subjected to continuous stress. Their reinforced design minimizes the need for frequent maintenance or replacement. However, regular inspections remain important to ensure long-term performance.
5. Cost vs. Benefit
While heavy-duty encoders require a higher initial investment, their long-term benefits often outweigh the cost. The durability reduces the need for replacements, ultimately lowering the cost of downtime and maintenance over time.
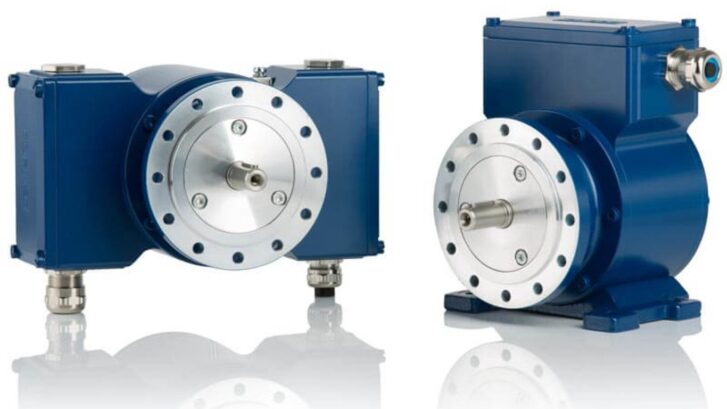
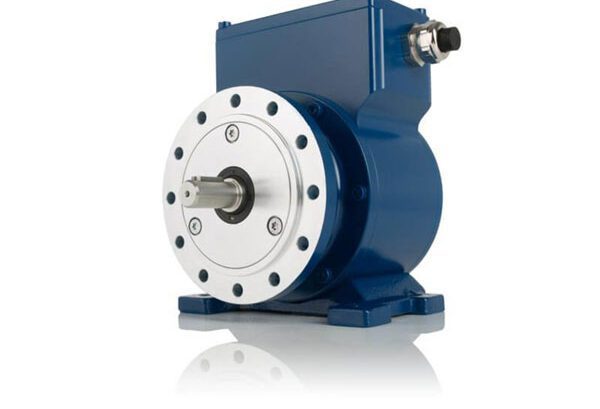
Standard Encoders: Reliable, Yet Lightweight
1. Design and Suitability
Manufacturers design standard encoders for more controlled environments. These encoders are lighter, often using aluminum or plastic components, which makes them easier to handle and install. Although they lack the heavy-duty protection, they perform effectively in environments where physical stress is minimal.
Standard encoders excel in settings with stable temperature, dust, and humidity levels. Their simpler design makes installation straightforward, reducing the complexity of setup and maintenance.
2. Environmental Resistance
Standard encoders have lower IP ratings, typically around IP50 to IP54. These encoders provide basic protection against dust and minor splashes of water. However, they are not suitable for environments where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or heavy dust is common.
Moreover, standard encoders function best in environments with stable temperatures. Exposure to extreme heat, cold, or temperature fluctuations can impair their performance, limiting their suitability for industries that require extreme durability.
3. Applications in Controlled Environments
Standard encoders perform well in controlled environments, including:
- Factory Automation: Standard encoders deliver accurate feedback for tasks like conveyor belts and automated assembly lines in stable industrial settings.
- Robotics: Robots in indoor settings rely on standard encoders for position sensing or movement tracking, where environmental stressors are minimal.
- Packaging and Printing: These applications demand precise motion control, which standard encoders easily provide in controlled, clean environments.
4. Lifespan and Maintenance
The lifespan of a standard encoder can extend for years if it’s used within its design parameters. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and inspection, can ensure its longevity. However, if a standard encoder is exposed to higher-than-expected stress or contamination, it will require more frequent maintenance or replacement.
5. Cost Effectiveness
Standard encoders offer a budget-friendly option for industries that don’t require rugged durability. Their lower price makes them an excellent choice for manufacturers looking to optimize expenses in controlled environments.
Choosing Between Heavy-Duty and Standard Encoders
Selecting the right encoder depends on understanding your operational environment and specific system demands. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Operational Environment
- If dust, moisture, extreme temperatures, or physical shock is a concern, heavy-duty encoders will be more appropriate. In controlled environments, standard encoders will suffice.
- Load and Stress
- Applications involving heavy machinery, continuous movement, or vibration benefit from the durability of heavy-duty encoders. Lighter tasks, such as robotics or packaging, are more suited for standard encoders.
- Budget Considerations
- Heavy-duty encoders may cost more upfront, but their durability makes them a better long-term investment in demanding environments. For controlled applications, standard encoders offer a more cost-effective solution.
- Maintenance and Downtime
- Heavy-duty encoders require less frequent maintenance, making them ideal for industries where downtime is costly. In comparison, standard encoders offer affordability but may need more frequent upkeep.
Conclusion
Heavy-duty and standard encoders differ in construction, environmental resistance, and application suitability. Heavy-duty encoders thrive in rugged environments, offering superior durability and longer lifespans under harsh conditions. On the other hand, standard encoders provide a reliable, cost-effective solution for controlled environments with stable conditions.
Choosing the right encoder is essential for optimizing system performance and minimizing downtime. By understanding your application’s specific needs and environmental demands, you can make an informed decision. Heavy-duty encoders provide a long-term solution for tough industries, while standard encoders are perfect for everyday tasks in controlled settings.
Both types of encoders play critical roles in various industries, ensuring that automated systems function with precision and reliability.